Proxmox + K3s Home Lab (Terraform + Ansible Automation)
Overview
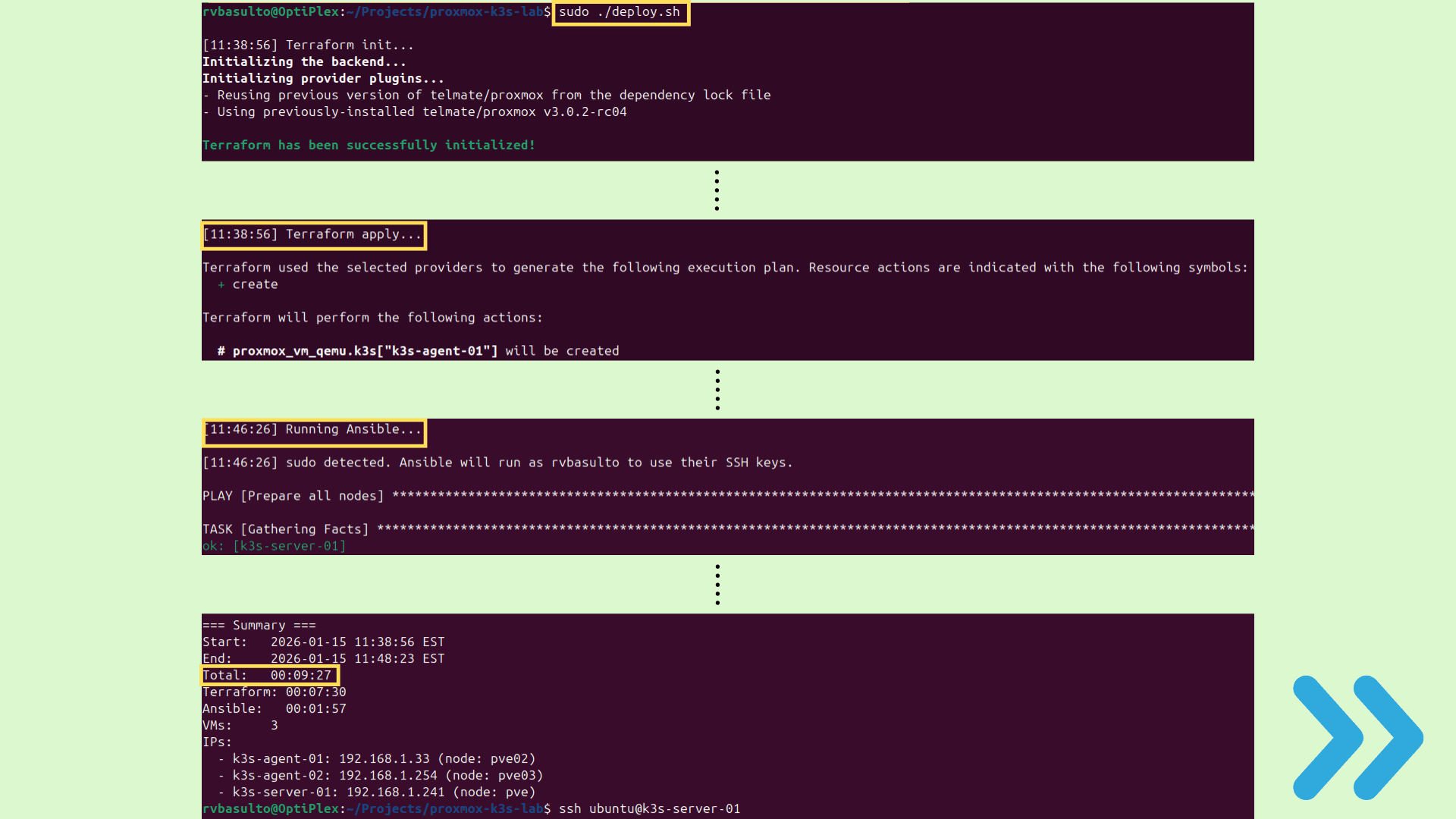
Built a fully automated Kubernetes home lab using Proxmox VE as the virtualization platform and K3s as the lightweight Kubernetes distribution. The main goal of this project was reproducibility: if the entire environment disappears, the full cluster can be recreated in minutes with the same configuration and results.
This lab simulates real-world DevOps workflows by combining Infrastructure as Code (Terraform) and Configuration Management (Ansible) to provision and configure a multi-node Kubernetes cluster consistently, without manual setup inside Proxmox.
Goals
- Provision a complete Kubernetes cluster from scratch using IaC.
- Eliminate manual VM creation and OS setup tasks.
- Create a repeatable deployment workflow suitable for scaling and experimentation.
- Practice production-style automation patterns (separation of responsibilities, idempotency, inventory automation).
Architecture
The lab provisions 3 virtual machines in Proxmox:
- 1 Control Plane (K3s Server)
- 2 Worker Nodes (K3s Agents)
All VMs are created from a Cloud-Init Ubuntu template, enabling automated first-boot configuration such as SSH access and network initialization.
Tech Stack
- Proxmox VE (virtualization / compute layer)
- Terraform (VM provisioning using Proxmox provider)
- Ansible (OS preparation + K3s installation orchestration)
- K3s Kubernetes (lightweight Kubernetes distribution)
- Linux / SSH / Bash (automation and troubleshooting)
- Cloud-Init (bootstrap configuration for VMs)
Implementation Details
1) Golden Image + Cloud-Init Template
Created a reusable Ubuntu template in Proxmox using Cloud-Init, allowing each VM clone to boot with predefined configuration and minimal manual intervention.
Key automation features:
- SSH key injection for secure access
- Standardized VM baseline configuration
- Fast cloning for consistent node creation
2) Infrastructure Provisioning with Terraform
Terraform provisions the full infrastructure layer inside Proxmox:
- VM creation from template
- CPU/RAM/Disk sizing per node role
- Network configuration and VM naming strategy
- Cluster-ready topology (server + agents)
This provides a clean, version-controlled workflow where the full lab can be deployed and destroyed safely.
3) Configuration Management with Ansible
After Terraform creates the VMs, Ansible completes the post-provisioning configuration:
- Updates packages and prepares the OS
- Disables swap and applies kernel parameters required for Kubernetes
- Configures system-level dependencies
- Installs and initializes K3s Server
- Joins worker nodes automatically using a secure token workflow
- Verifies node readiness and cluster status
Ansible is organized using reusable roles and structured inventories for maintainability.
Key DevOps Practices Applied
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with Terraform
- Separation of responsibilities
- Terraform handles infrastructure lifecycle
- Ansible handles configuration and software installation
- Idempotent automation
- Safe re-runs without breaking existing nodes
- Reproducibility
- Consistent results across deployments
- Production-style troubleshooting
- SSH host key issues, network/IP discovery, guest agent behavior, cloud-init behavior
Challenges & Troubleshooting Highlights
- Debugged VM networking and IP reporting issues when using Proxmox + Cloud-Init.
- Investigated QEMU Guest Agent limitations and timing issues during provisioning.
- Resolved SSH host key conflicts when recreating nodes frequently (known_hosts management).
- Improved deployment reliability by tuning provisioning wait timeouts and sequencing.
Results / Outcome
- Fully working multi-node Kubernetes cluster running on Proxmox.
- Cluster can be rebuilt quickly with consistent configuration using Terraform + Ansible.
- Created a reliable lab environment to practice Kubernetes deployments, networking, and DevOps workflows.
- Strong foundation for future expansions (Ingress, Load Balancing, GitOps, Monitoring, CI/CD).
Next Improvements
- Add Ingress Controller and DNS-based access inside the lab.
- Deploy a GitOps workflow (ArgoCD or Flux).
- Add monitoring stack: Prometheus + Grafana.
- Introduce centralized logging (Loki or ELK).
- Add CI/CD to automatically deploy apps into the cluster.